Circulatory System in Frogs / Frogs (Amphibians) Equipped with Pictures
The circulatory system in amphibians has similarities with other vertebrate animals which have a closed circulatory system. In the amphibious class, the circulatory system experiences differences while still in the form of tadpoles and the shape of adult frogs. When still tadpoles, the circulatory system is like the circulatory system of the fish where the heart only consists of two rooms (1 atrium and 1 ventricle). As for being an adult frog, the circulatory system has a heart with 3 chambers (2 atria and 1 ventricle).
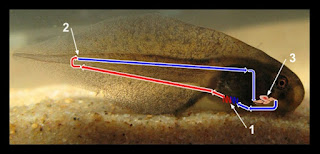
Figure 1. Circulatory system in tadpoles. (1) gills, gas exchange occurs; (2) Oxygen points run out; (3) A heart consisting of two contours. Red = oxygen-rich blood; Blue = blood rich in carbon dioxide.
The mechanism of the frog's circulatory system is a closed circulatory system and multiple blood circulation. Scavenging the double circulatory system is that blood passes through the heart twice in one circulation.
First, blood from the heart will go to the lungs and then back to the heart. Secondly, blood from the whole body will go to the heart and will be circulated back throughout the body.
Frogs have a heart consisting of three chambers, namely two atria (right atrium and left atrium) and one ventricle. Between the atrium and ventricle there is a valve that serves to prevent blood in the ventricles from flowing back into the atrium.
Figure 2. Frog's circulatory system.
Low blood oxygen from various tissues and organs of the body will flow to the venous sinus to the right atrium. Next, the blood from the right atrium will flow to the ventricles, then it will go to the pulmonary artery and enter the lungs.
In the lungs, carbon dioxide gas will be released and oxygen gas will be bound. From the lungs, the blood flow will flow to the pulmonary vein and then to the left atrium. The circulatory process that occurs is called small blood circulation.
The next stage is the blood flow from the left atrium, the blood will flow to the ventricles. In this ventricle room, a mixture of blood containing oxygen with blood containing carbon dioxide in a small amount occurs.
Blood flow from the ventricles will come out through the tractus arteriosus (pulse) to the aorta branching left and right. Each of these aortas branch out into three main arteries, namely (1) the anterior artery (carotid) which functions to drain blood to the head and to the brain, (2) the aortic arch that drains blood to all internal tissues and organs in the body, and ( 3) the posterior arteries that function to drain blood to the skin and lungs.
Frogs have blood consisting of blood plasma and blood cells. The blood plasma content is water, blood protein, and mineral salts. Frog blood cells consist of erythrocytes (red blood cells) and leukocytes (white blood cells). Erythrocytes in frogs have a nucleus and contain hemoglobin which functions to bind oxygen.
Figure 1. Circulatory system in tadpoles. (1) gills, gas exchange occurs; (2) Oxygen points run out; (3) A heart consisting of two contours. Red = oxygen-rich blood; Blue = blood rich in carbon dioxide.
The mechanism of the frog's circulatory system is a closed circulatory system and multiple blood circulation. Scavenging the double circulatory system is that blood passes through the heart twice in one circulation.
First, blood from the heart will go to the lungs and then back to the heart. Secondly, blood from the whole body will go to the heart and will be circulated back throughout the body.
Frogs have a heart consisting of three chambers, namely two atria (right atrium and left atrium) and one ventricle. Between the atrium and ventricle there is a valve that serves to prevent blood in the ventricles from flowing back into the atrium.
Figure 2. Frog's circulatory system.
Low blood oxygen from various tissues and organs of the body will flow to the venous sinus to the right atrium. Next, the blood from the right atrium will flow to the ventricles, then it will go to the pulmonary artery and enter the lungs.
In the lungs, carbon dioxide gas will be released and oxygen gas will be bound. From the lungs, the blood flow will flow to the pulmonary vein and then to the left atrium. The circulatory process that occurs is called small blood circulation.
The next stage is the blood flow from the left atrium, the blood will flow to the ventricles. In this ventricle room, a mixture of blood containing oxygen with blood containing carbon dioxide in a small amount occurs.
Blood flow from the ventricles will come out through the tractus arteriosus (pulse) to the aorta branching left and right. Each of these aortas branch out into three main arteries, namely (1) the anterior artery (carotid) which functions to drain blood to the head and to the brain, (2) the aortic arch that drains blood to all internal tissues and organs in the body, and ( 3) the posterior arteries that function to drain blood to the skin and lungs.
Frogs have blood consisting of blood plasma and blood cells. The blood plasma content is water, blood protein, and mineral salts. Frog blood cells consist of erythrocytes (red blood cells) and leukocytes (white blood cells). Erythrocytes in frogs have a nucleus and contain hemoglobin which functions to bind oxygen.


Post a Comment